The Best Way to Learn Java

A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
Java remains one of the most popular programming languages worldwide. Its versatility spans web applications, mobile development, and enterprise systems. Beginners often feel overwhelmed when starting their Java journey. This comprehensive guide breaks down the best way to learn Java into manageable steps.
We'll cover everything from setting up your environment to building your first projects. You'll discover proven learning strategies and avoid common pitfalls. By the end, you'll have a clear roadmap for mastering Java programming.
Why Learn Java Programming in 2025
Java continues to rank among the top programming languages in industry demand. Its "write once, run anywhere" capability makes it incredibly versatile. Companies value Java developers for both their programming skills and problem-solving abilities.
Learning Java offers several significant advantages for beginners:
- Strong foundation in object-oriented programming principles
- Extensive community support and abundant learning resources
- Excellent job prospects across various industries
- Transferable skills that apply to other programming languages
- Robust standard library that simplifies development
Java knowledge provides valuable skills for web development. Understanding programming fundamentals enhances your ability to customize platforms like Webflow for more complex projects.
Understanding Java Fundamentals
Before diving into code, understanding the Java platform components helps build a solid foundation. These core elements work together to create the complete Java development and runtime environment.
Key Components of the Java Platform
The Java platform consists of several crucial components that work together to support development and execution. Understanding how these parts interact helps troubleshoot issues and optimize your development workflow.
Java Development Kit (JDK)
- Function: Development tools including compiler and debugger
- Why It Matters: Required to write and build Java applications
Java Runtime Environment (JRE)
- Function: Runtime environment for executing Java applications
- Why It Matters: Needed to run compiled Java programs
Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
- Function: Executes Java bytecode on different platforms
- Why It Matters: Enables platform independence ("write once, run anywhere")
Standard Library (Java API)
- Function: Pre-built classes and packages
- Why It Matters: Provides ready-to-use functionality
This framework ensures Java programs work consistently across different operating systems and devices. The platform's architecture simplifies both development and deployment processes.
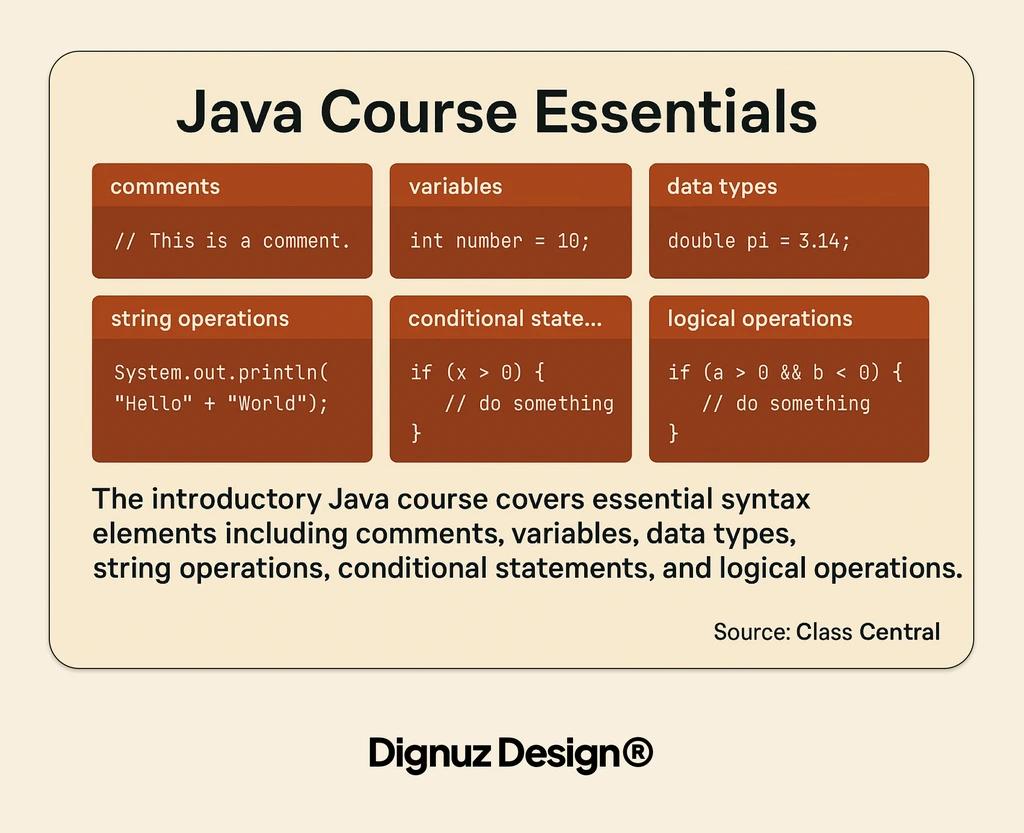
Java Syntax Basics for Beginners
The introductory Java course covers essential syntax elements including comments, variables, data types, string operations, conditional statements, and logical operations. (Source: Class Central)
Here's a simple Java program demonstrating basic syntax:
// This is a comment
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Variable declaration
String message = "Hello, Java Beginner!";
// Print to console
System.out.println(message);
// Conditional statement
if (message.contains("Beginner")) {
System.out.println("Welcome to your Java journey!");
}
}
}Java syntax follows consistent patterns. Every program has at least one class. The main method serves as the entry point. Statements end with semicolons. These fundamentals remain consistent as you progress to more complex concepts.
Step-by-Step Learning Path for Java Beginners
Success in learning Java requires a structured approach. Following a step-by-step path ensures you build knowledge progressively without gaps. This methodical progression helps avoid common frustrations.
Phase 1: Setting Up Your Java Development Environment
Setting up your development environment correctly saves hours of frustration later. Several options exist depending on your preferences and learning goals. Each option offers different advantages for beginners.
JDK + Basic Text Editor
- Best For: Complete beginners
- Advantages: Forces understanding of compilation process
- Disadvantages: Limited assistance, time-consuming
IntelliJ IDEA (Community)
- Best For: Serious learners
- Advantages: Professional features, excellent support
- Disadvantages: Steeper learning curve
Eclipse
- Best For: Multi-language developers
- Advantages: Free, highly customizable
- Disadvantages: Sometimes slower, complex interface
Online IDEs (Replit, etc.)
- Best For: Quick starters
- Advantages: No setup required, immediate coding
- Disadvantages: Limited offline capabilities
Beginners often find online coding platforms ideal for starting. They eliminate setup complexities while you focus on learning syntax. As you progress, transitioning to a professional IDE provides more powerful tools.
Phase 2: Mastering Java Syntax and Core Concepts
Beginners learn Java most effectively through project-based syntax drills, such as cosmic message customization and error correction exercises. (Source: CodeSignal)
Core Java concepts every beginner should master include:
- Variables and Data Types - Understanding primitive types vs. objects
- Control Flow - Mastering if/else statements, loops, and switch cases
- Object-Oriented Programming - Classes, objects, inheritance, and polymorphism
- Exception Handling - Learning to handle errors gracefully
- Collections Framework - Working with lists, sets, and maps
The most effective learning approach combines concept explanations with immediate practice. Try writing code examples as you learn each concept. This reinforcement helps build stronger neural connections.
Phase 3: Building Your First Java Projects
After grasping the basics, simple projects cement your understanding. Start with console applications before moving to more complex projects. This progression builds confidence while reinforcing core concepts.
Beginner
- Example Projects: Calculator, Number Guessing Game
- Concepts Practiced: Variables, Input/Output, Control Flow
Intermediate
- Example Projects: To-Do List, Address Book
- Concepts Practiced: Classes, Arrays, File I/O
Advanced Beginner
- Example Projects: Simple Text Editor, Basic Database
- Concepts Practiced: Collections, Exception Handling
Project-Based Learning
- Example Projects: Student Enrollment System
- Concepts Practiced: HashMap, ArrayList, Real-world Applications
Building projects answers the critical question: What makes the difference between theoretical knowledge and practical skill? The answer lies in application and practice. Projects transform abstract concepts into tangible results.

Top Java Learning Resources for Beginners
With countless resources available, finding quality learning materials matters. The right resources accelerate your progress significantly. Quality matters more than quantity when selecting learning materials.
Online Courses and Structured Learning Paths
Structured learning paths offer a comprehensive approach to mastering Java. CodeSignal's Java Beginner Path offers 7 courses with 184 coding practices spanning 12 hours of content and has over 9,555 enrolled learners. (Source: CodeSignal)
Interactive Platforms
- Top Options: CodeSignal, Codecademy, JetBrains Academy
- Best Features: Immediate feedback, integrated IDE
- Investment: Free-$199/month
Video Courses
- Top Options: Udemy, Coursera, YouTube
- Best Features: Visual learning, instructor guidance
- Investment: Free-$200 one-time
University MOOCs
- Top Options: Helsinki MOOC, MIT OpenCourseware
- Best Features: Academic rigor, comprehensive coverage
- Investment: Mostly free
Coding Bootcamps
- Top Options: CodeCamp, Springboard
- Best Features: Intensive, career-focused
- Investment: $1,000-$10,000
When selecting resources, consider your learning style. Visual learners thrive with video tutorials. Hands-on learners prefer interactive platforms with coding exercises. The best approach often combines multiple resource types.
Practice Platforms and Coding Challenges
Theory alone isn't enough. Regular practice solidifies understanding and builds problem-solving skills. Research shows that consistent daily practice of even just 20 minutes significantly improves skill retention in programming.
Top practice platforms include:
- HackerRank - Graduated difficulty challenges with Java focus
- LeetCode - Algorithm and data structure problems favored by employers
- Codewars - Community-created challenges with "kata" ranking system
- CodeSignal - Structured practice with immediate feedback
These platforms gamify learning with achievement systems. The competitive element motivates consistent practice. Many developers maintain daily streaks to build coding habits.
Books and Documentation for Reference
Despite the digital age, books remain valuable learning tools. They offer depth that online tutorials sometimes lack. Good programming books provide comprehensive coverage and timeless principles.
Beginner-friendly Java books include:
- "Head First Java" - Visual approach with engaging exercises
- "Java: A Beginner's Guide" by Herbert Schildt - Clear explanations with examples
- "Effective Java" by Joshua Bloch - Best practices for intermediate learners
The official Java documentation provides authoritative reference material. Bookmark docs.oracle.com/javase for detailed API information. Learning to navigate documentation is itself a valuable skill for developers.
Effective Java Learning Strategies
The learning approach matters as much as the resources. Effective strategies accelerate progress and deepen understanding. Smart techniques can dramatically reduce learning time.
Balancing Theory with Hands-on Practice
Finding the right balance between theory and practice challenges many beginners. Too much theory without application leads to forgetting. Too much coding without understanding creates knowledge gaps.
The CodeSignal learning app helps maintain this balance by integrating theory lessons directly with practice exercises, allowing students to immediately apply what they've learned in a structured environment. (Source: CodeSignal)
An effective approach follows this pattern:
Learn a concept through explanation and examples
Practice immediately with simple exercises
Apply the concept in a slightly larger context
Review and reinforce through repetition
This iterative approach builds lasting knowledge. The "learning loop" of concept-practice-application-review creates stronger neural connections. Consistency matters more than marathon study sessions.
Joining Java Communities and Finding Mentors
Learning accelerates dramatically with community support. Active Java communities include:
- Stack Overflow - Technical questions and answers
- Reddit's r/learnjava - Beginner-friendly discussion forum
- Discord programming servers - Real-time chat with other learners
- Local meetup groups - In-person networking and learning
Finding a mentor provides immense value. The power of guidance from experienced developers cannot be overstated. Mentors help avoid common pitfalls and provide personalized feedback on your code and learning approach.
Common Beginner Mistakes to Avoid
Awareness of common mistakes saves time and frustration. Beginners frequently encounter these challenges that can slow down their progress and cause unnecessary difficulties.
Trying to memorize everything
- Why It Happens: Believing coding requires perfect recall
- Better Approach: Focus on concepts; use documentation for specifics
Not practicing daily
- Why It Happens: Inconsistent schedule, motivation issues
- Better Approach: Set small, achievable daily coding goals
Copy-pasting without understanding
- Why It Happens: Rushing to complete exercises
- Better Approach: Type code manually, explain each line to yourself
Skipping fundamentals for frameworks
- Why It Happens: Desire to build impressive projects quickly
- Better Approach: Master core Java before approaching frameworks
Not reading error messages
- Why It Happens: Intimidation by technical language
- Better Approach: Learn to decode errors; they contain valuable hints
Avoiding these pitfalls saves countless hours of frustration. Patient progress builds stronger foundations than rushing. Many successful developers credit their disciplined learning approach for their long-term success.
From Java Basics to Advanced Applications
Once you've mastered the basics, a world of possibilities opens. The progression from beginner to intermediate Java developer follows a natural path. Your next steps depend on your specific interests and goals.
Progression Path After Learning Fundamentals
After core Java mastery, consider these progression paths:
- Web Development - Learning Spring Boot or Jakarta EE
- Mobile Development - Building Android apps with Java
- Desktop Applications - Creating GUI apps with JavaFX
- Data Engineering - Working with big data using Java
- Enterprise Applications - Building robust business systems
Each path requires additional frameworks and tools. Your choice depends on career goals and personal interests. Most Java developers specialize in one or two areas while maintaining general knowledge across the ecosystem.
Real-World Java Project Ideas for Beginners
The curriculum includes HashMap and ArrayList implementations for real-world applications like student enrollment systems. (Source: CodeSignal)
Practical projects apply your knowledge while building your portfolio. Consider these beginner-friendly project ideas:
- Personal Budget Tracker - Practice file I/O and data management
- Simple Chat Application - Learn networking basics
- Task Management System - Implement CRUD operations
- Weather Data Analyzer - Work with APIs and data processing
- E-commerce Product Catalog - Build database interactions
Each project teaches valuable skills beyond syntax. You'll learn software design, debugging techniques, and testing strategies. The practical experience gained from these projects translates directly to professional development work.
Next Steps
Learning Java opens doors to countless opportunities in software development. This guide provided a structured approach to mastering Java fundamentals.
The best way to learn Java combines:
- A structured learning path with quality resources
- Regular, deliberate practice with real coding exercises
- Building progressively complex projects
- Community engagement and mentor guidance
- Consistent effort over time
Remember that learning programming is a marathon, not a sprint. Celebrate small wins along your journey. Each concept mastered brings you closer to Java proficiency.
As you continue your Java learning journey, consider these next steps:
- Join an open-source Java project to gain collaborative experience
- Create a personal coding challenge calendar for consistent practice
- Explore specialized Java applications in your interest areas
- Connect with local Java developer communities for networking
- Consider Java certification to validate your skills formally
Is Webflow easy to use for non-programmers? Yes, but your Java knowledge gives you a significant advantage in customizing and extending web platforms beyond their standard capabilities.
Whether your goal is career advancement, personal projects, or simply expanding your technical knowledge, Java provides a solid foundation for your programming journey. Start small, stay consistent, and build your skills day by day.